CASE OF THE MONTH
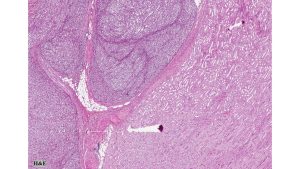
A 38-year-old male presented with a history of persisting right flank pain. Ultrasonography revealed a 10 cm mass in the mid-portion of the right kidney at the corticomedullary junction. A CT-guided biopsy revealed a spindle cell neoplasm of uncertain malignancy. The patient underwent a right nephrectomy, which revealed a 10×6×5 cm solid tumor with vascular invasion. On gross examination, the tumor was grayish white with areas of hemorrhage and necrosis.
Contributors :
Ekta Jain, MD, PostDoctoral Clinical Research Fellow, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama
Rodolfo Monitorini, MD, IFCAP, Molecular Medicine and Cell Therapy Foundation, Università Politecnica delle Marche, Ancona, Italy
Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD, FCAP, Professor & Chair of Pathology, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama
What would your diagnosis be?
a. Monophasic spindle cell synovial sarcoma, provided that a molecular study shows rearrangement in the SYT-SSX gene
b. Renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid dedifferentiation
c. Sarcomatoid variant of urothelial carcinoma
d. Adult Wilms tumor with predominant stromal component
e. No need for additional ancillary study and make a diagnosis of undifferentiated sarcoma
Which of the following translocations is characteristically seen in this tumor?
a. t(X;18)(p11;q11)
b. t(11;22)(q24;q12)
c. t(12;16)(q13;p11)
d. t(2;13)(q35;q14)
1. Correct answer: a. Monophasic spindle cell synovial sarcoma, provided that a molecular study shows rearrangement in the SYT-SSX gene
2. Correct answer: a. t(X;18)(p11;q11)
Monophasic spindle cell synovial sarcoma of the kidney
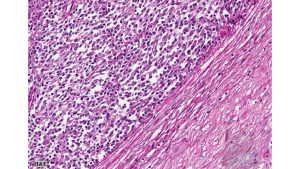
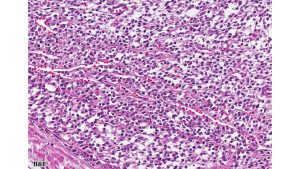
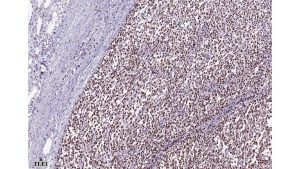
Histologic examination revealed densely cellular fascicles of monomorphic spindle cells with indistinct borders, oval nuclei and scant cytoplasm. The background showed necrosis and areas of hemorrhage. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed tumor cells positive for vimentin, CD99, BCL-2 and TLE1, while negative for CEA, EMA, desmin, chromogranin, synaptophysin, enolase, S-100, CD10, CD117, Caldesmon, beta-catenin, PAX2, and WT-1.
Primary synovial sarcoma of the kidney is exceedingly rare and often presents a diagnostic challenge due to morphologic overlap with other renal spindle cell tumors, such as sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid urothelial carcinoma, and other primary renal sarcomas (e.g., leiomyosarcoma or malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor). The monophasic spindle cell variant lacks epithelial components, making differentiation particularly difficult without molecular testing. Immunohistochemistry often demonstrates expression of TLE1, CD99, vimentin, and BCL-2, but these markers are not entirely specific. The definitive diagnosis hinges on detecting the characteristic t(X;18)(p11;q11) translocation, which results in the SS18-SSX fusion (typically SSX1 or SSX2) via FISH or RT-PCR.. These tumors tend to behave aggressively, with potential for local recurrence and distant metastasis, particularly to the lungs and liver. Long-term follow-up is essential, and optimal management often requires a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating surgery and consideration of systemic therapy in selected cases.
1. Mastoraki A, Schizas D, Karavolia DM, et al. Primary Synovial Sarcoma of the Kidney: Diagnostic Approach and Therapeutic Modalities for a Rare Nosological Entity. J Pers Med. 2022 Sep 2;12(9):1450.
2. Cai HJ, Cao N, Wang W, Kong FL, Sun XX, Huang B. Primary renal synovial sarcoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 2019 Oct 6;7(19):3098-103.
3. Pitino A, Squillaci S, Spairani C, et al. Primary synovial sarcoma of the kidney. A case report with pathologic appraisal investigation and literature review. Pathologica. 2011 Oct;103(5):271-8.
Ekta Jain, MD, PostDoctoral Clinical Research Fellow, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama
Rodolfo Monitorini, MD, IFCAP, Molecular Medicine and Cell Therapy Foundation, Università Politecnica delle Marche, Ancona, Italy
Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD, FCAP, Professor & Chair of Pathology, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama
Kidney
Primary renal synovial sarcoma, monophasic, TLE1, SS18-SSX, aggressive